Man hört ja immer wieder, dass Alfonso Cuaróns Meisterwerk “Gravity” vor allem durch seine realistische Darstellung des Astronauten-Alltags im Weltraum besticht. Das ist für den erdgebundenen Laien natürlich schwer zu überprüfen, daher hat die NASA nun am vergangenen Sonntag, passend zu den Oscars 2014, Real-Life-Bilder ihrer Weltraummissionen veröffentlicht, die einem die Kinnlade aus dem Gesicht fallen lassen. Wer “Gravity” schon vorher mochte, wird es anhand dieser Bilder nur noch mehr lieben.
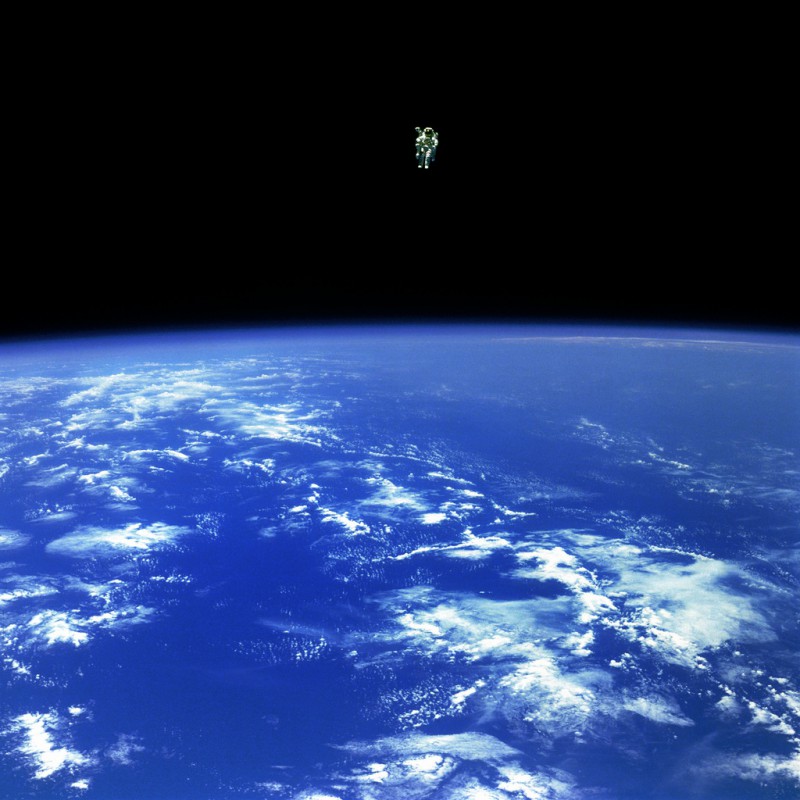
Das Foto oben zeigt einen echten freien Weltraumflug:
Mission Specialist Bruce McCandless II, is seen further away from the confines and safety of his ship than any previous astronaut has ever been. This space first was made possible by the Manned Manuevering Unit or MMU, a nitrogen jet propelled backpack. After a series of test maneuvers inside and above Challenger’s payload bay, McCandless went “free-flying” to a distance of 320 feet away from the Orbiter. This stunning orbital panorama view shows McCandless out there amongst the black and blue of Earth and space. (02/12/1984)
Alle Bilder der Real Gravity Fotostrecke findet ihr auf dem offiziellen Flickr-Account der NASA. Hier aber erstmal mein persönliches Best-of (Erklärung jeweils unter dem Bild):
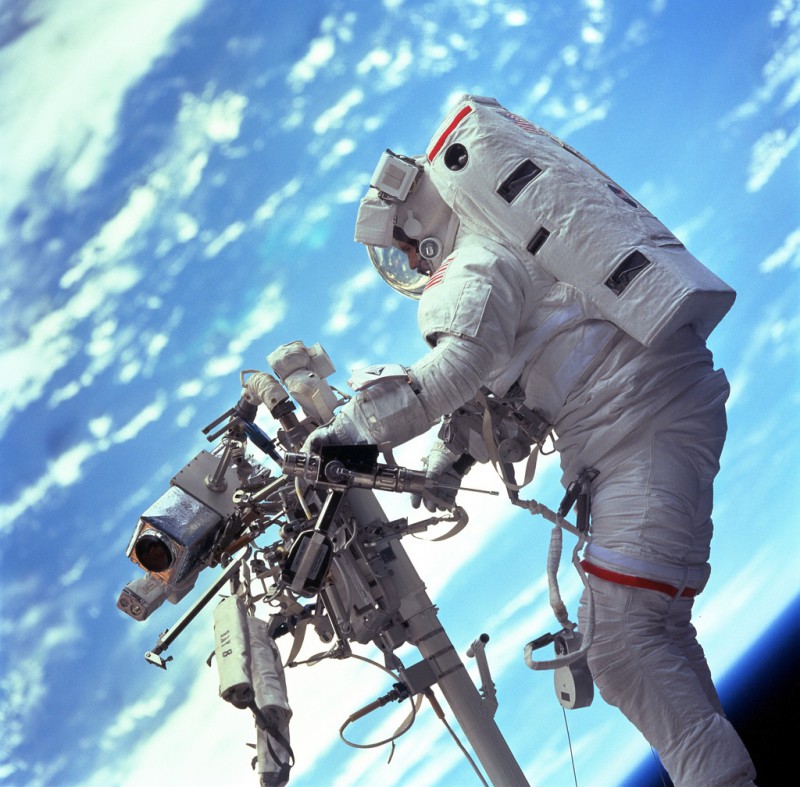
STS103-701-047 (19-27 December 1999) — Astronaut Steven L. Smith, payload commander, retrieves a power tool while standing on the mobile foot restraint at the end of the remote manipulator system (RMS). Many of the tools required to service the Hubble Space Telescope are stored on the handrail attached to the RMS visible in the photograph.
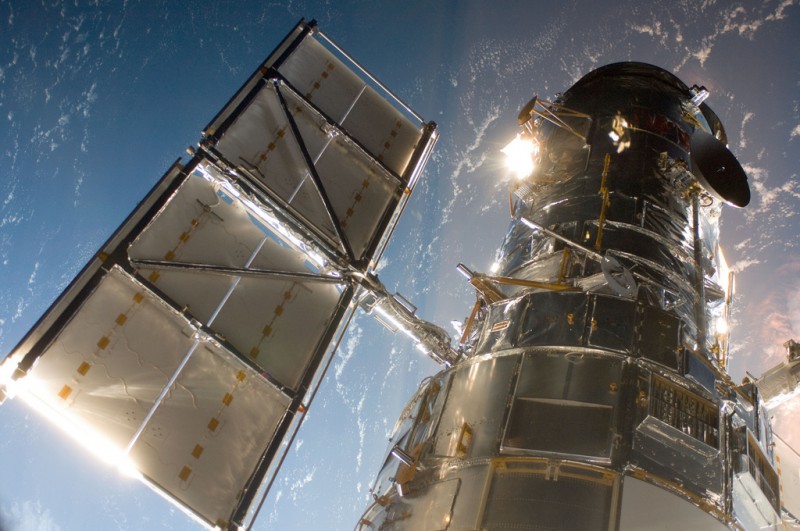
The Hubble Space Telescope in a picture snapped by a Servicing Mission 4 crewmember just after the Space Shuttle Atlantis captured Hubble with its robotic arm on May 13, 2009, beginning the mission to upgrade and repair the telescope.
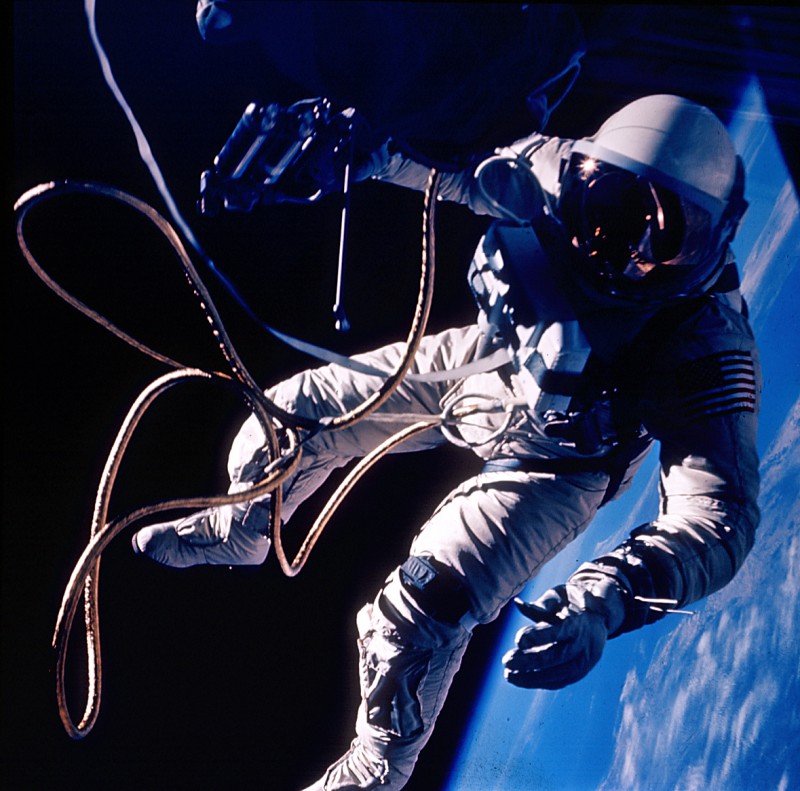
Ed White made the United States’ first spacewalk on 3 June 1965 during the Gemini 4 mission. The extra-vehicular activity (EVA) started at 19:45 UT (3:45 p.m. EDT) on the third orbit when White opened his hatch and used the hand-held manuevering oxygen-jet gun to push himself out of the capsule. The EVA started over the Pacific Ocean near Hawaii and lasted 23 minutes, ending over the Gulf of Mexico. Initially, White propelled himself to the end of the 8 meter tether and back to the spacecraft three times using the hand-held gun. After the first three minutes the fuel ran out and White manuevered by twisting his body and pulling on the tether. The photographs were taken by commander James McDivitt 19:54 UT (3:54 p.m. EDT) Over New Mexico (NASA photo ID S65-30433).
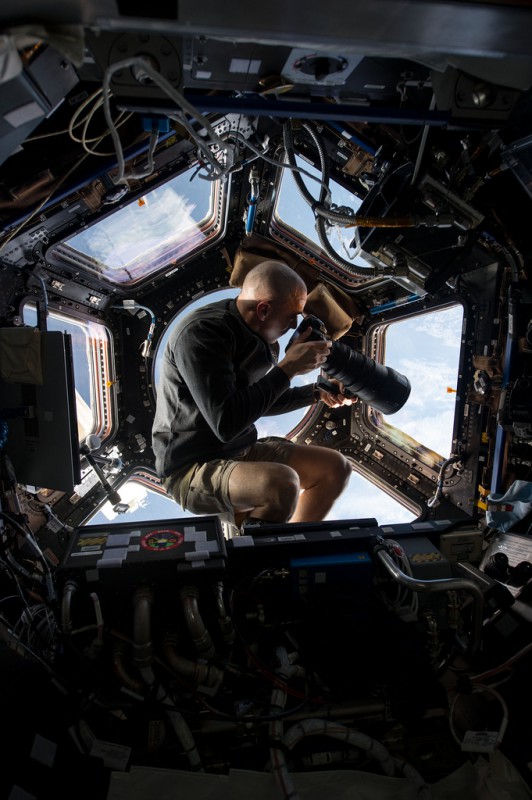
Inside the Cupola, NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, an Expedition 36 flight engineer, uses a 400mm lens on a digital still camera to photograph a target of opportunity on Earth some 250 miles below him and the International Space Station. Cassidy has been aboard the orbital outpost since late March and will continue his stay into September.
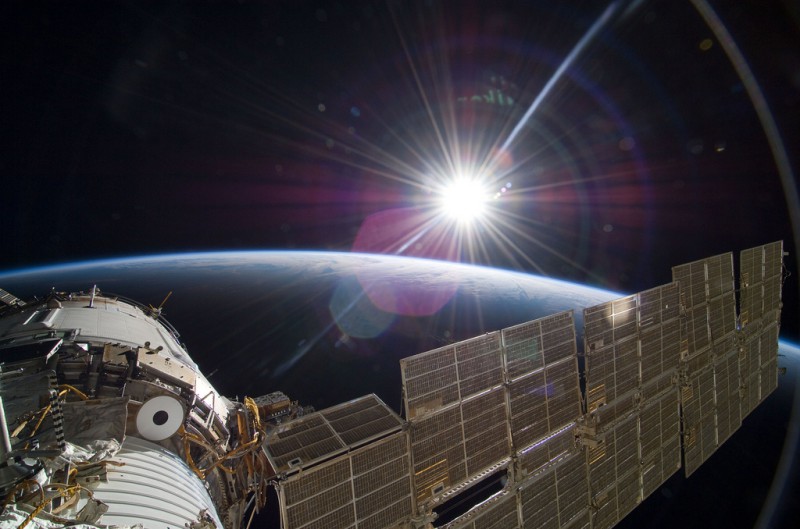
The bright sun greets the International Space Station in this Nov. 22 scene from the Russian section of the orbital outpost, photographed by one of the STS-129 crew members.
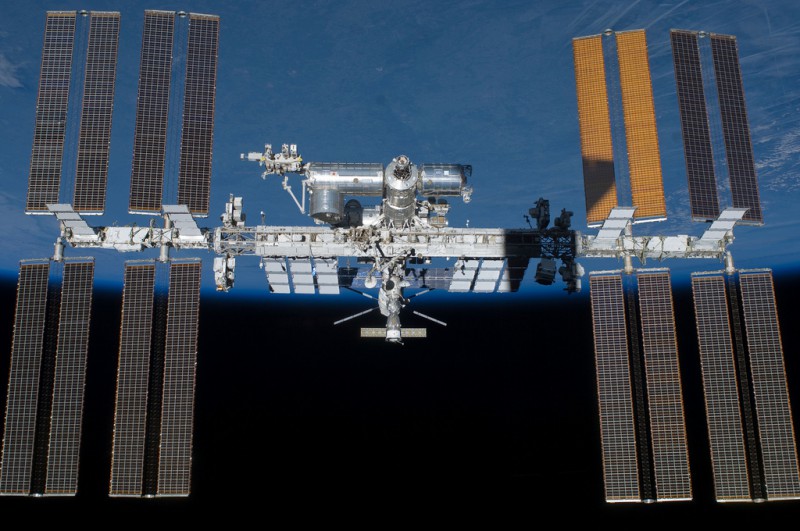
S134-E-010590 (29 May 2011) — Backdropped by Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space, the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by an STS-134 crew member on the space shuttle Endeavour after the station and shuttle began their post-undocking relative separation. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 11:55 p.m. (EDT) on May 29, 2011. Endeavour spent 11 days, 17 hours and 41 minutes attached to the orbiting laboratory.
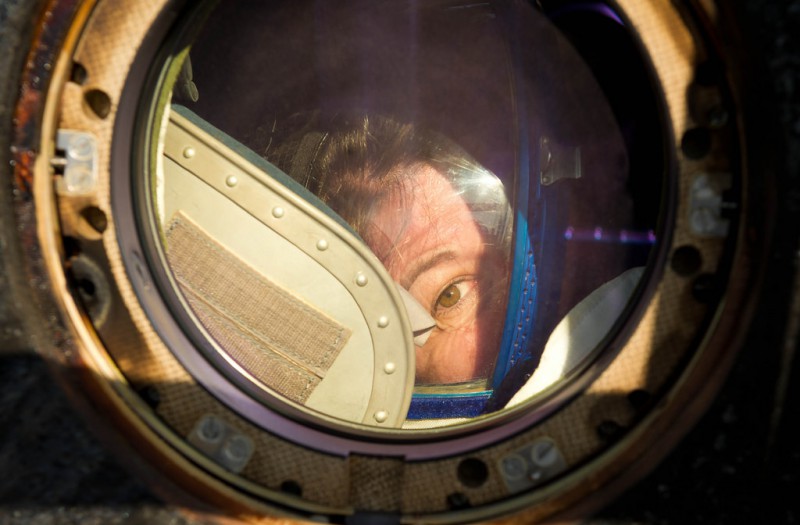
Expedition 27 Flight Engineer Cady Coleman peeks out of a window of the Soyuz TMA-20 spacecraft shortly after she and Commander Dmitry Kondratyev and Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli landed southeast of the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, May 24, 2011. NASA Astronaut Coleman, Russian Cosmonaut Kondratyev and Italian Astronaut Nespoli are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 26 and 27 crews.
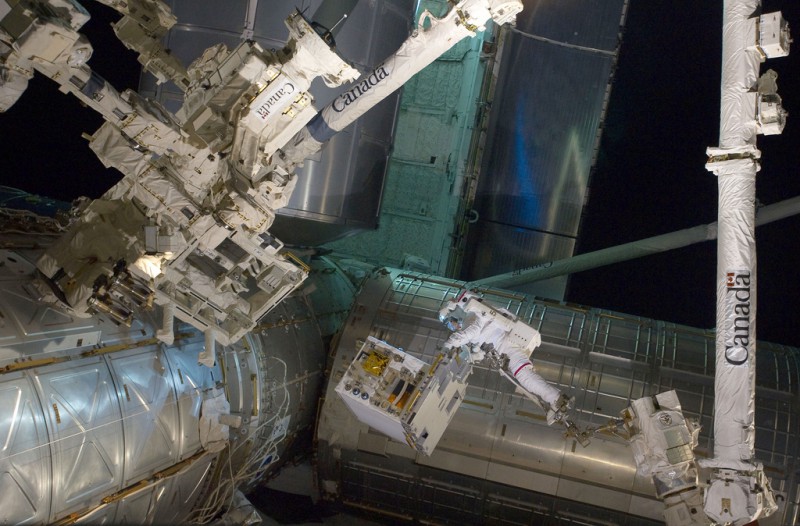
With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system’s robotic arm or Canadarm2, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum (frame center) holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload, which was the focus of one of the primary chores accomplished on a six and a half hour spacewalk on July 12. The failed pump module is with DEXTRE on left side of the photo. NASA astronauts Fossum and Ron Garan performed the six-hour, 31-minute spacewalk, which represents the final scheduled extravehicular activity during shuttle missions.
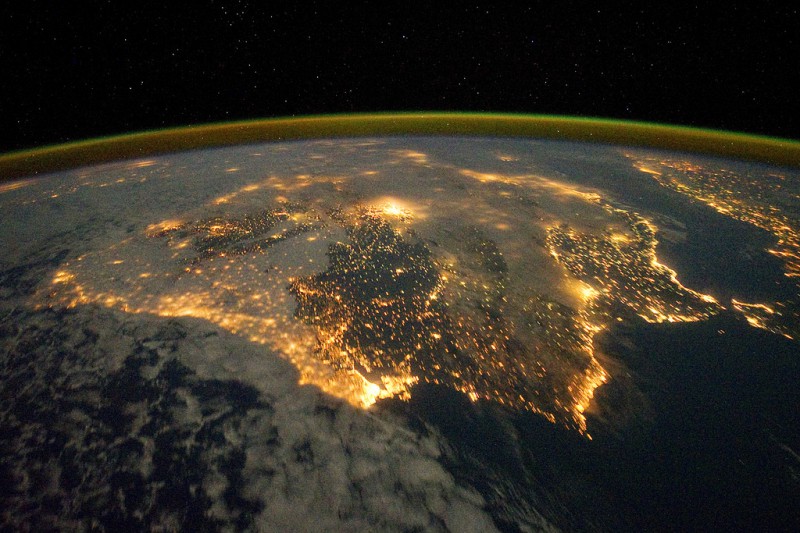
The city lights of Spain and Portugal define the Iberian Peninsula in this photograph from the International Space Station (ISS). Several large metropolitan areas are visible, marked by their relatively large and brightly lit areas, including the capital cities of Madrid, Spain—located near the center of the peninsula’s interior—and Lisbon, Portugal—located along the southwestern coastline. The ancient city of Seville, visible to the north of the Strait of Gibraltar, is one of the largest cities in Spain. The astronaut view is looking toward the east, and is part of a time-lapse series of images.